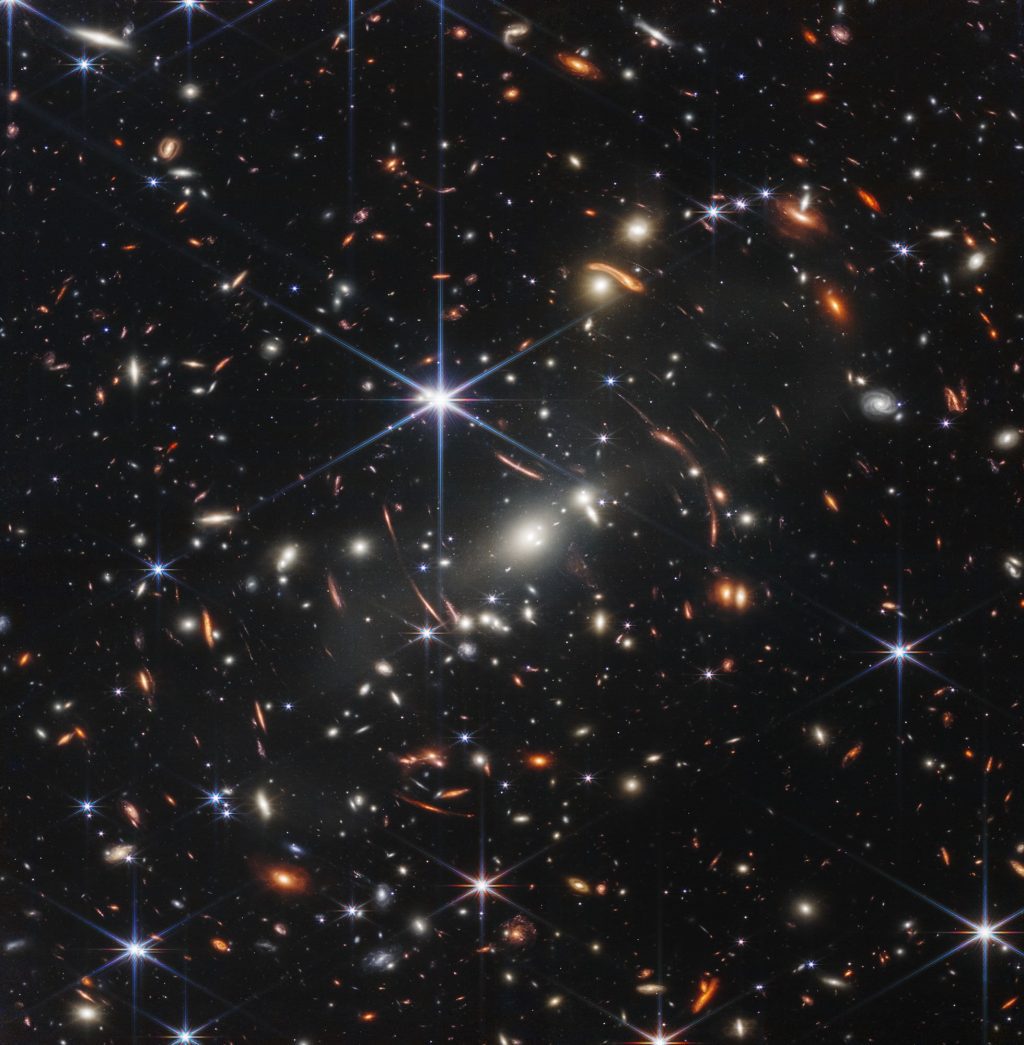
Drfirst years photo deep field beautifully detailed James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) released in June this year (photo above, click to enlarge), you can see the hosts of some of the oldest galaxies in the universe, shining like diamonds in a wide area of space and time …
In June 2022:
Looking deeper into the picture, a Canadian research team has now discovered Ball groups The most distant so far identified, which could contain the first and oldest stars in the universe. Finding these combinations is a task that Webb is specifically designed for.
According to Mia Moola, a member of the Dunlap Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Toronto (Canada) and co-lead author of the study:
Webb was built to find the first stars and galaxies and to help us understand the origins of the intricacies of the universe, such as the chemical elements and the building blocks of life.
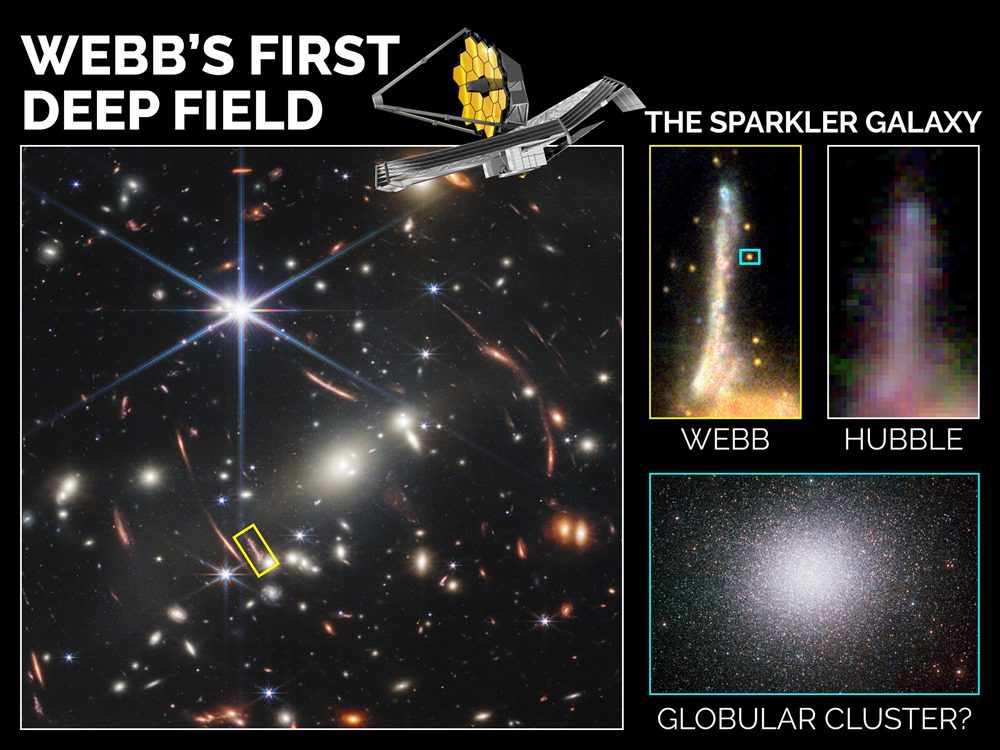
The researchers focused on a galaxy they dubbed the “Sparkling Galaxy” (Galaxy Sparkler), due to the tiny yellow and red twinkling dots from the star clusters surrounding it. Five of the twelve ‘flashes’ analyzed turned out to be so Ball groups, which are commonly found in the bulge and halo around galaxies and contain many ancient red stars. Because they are so close together, these groups are usually very stable and last for billions of years.
This discovery was made by CANUCS aptly named for Canadian Unbiased Cluster Survey NIRISS.
The football kits were determined by CANUCS due to the lack of spectral lines of oxygen in spectroscopic imaging data Neres (Near infrared imaging and non-slit spectrum) from Webb.
The location of the Sparkler Galaxy in Webb’s first deep field image. Top left, compared with Hubble images and zoom, bottom left, on a globular cluster. (NASA/ESA/El Calcada)
The presence of oxygen is important. If it is discovered, it indicates that the clusters were much smaller and actively involved in star formation.
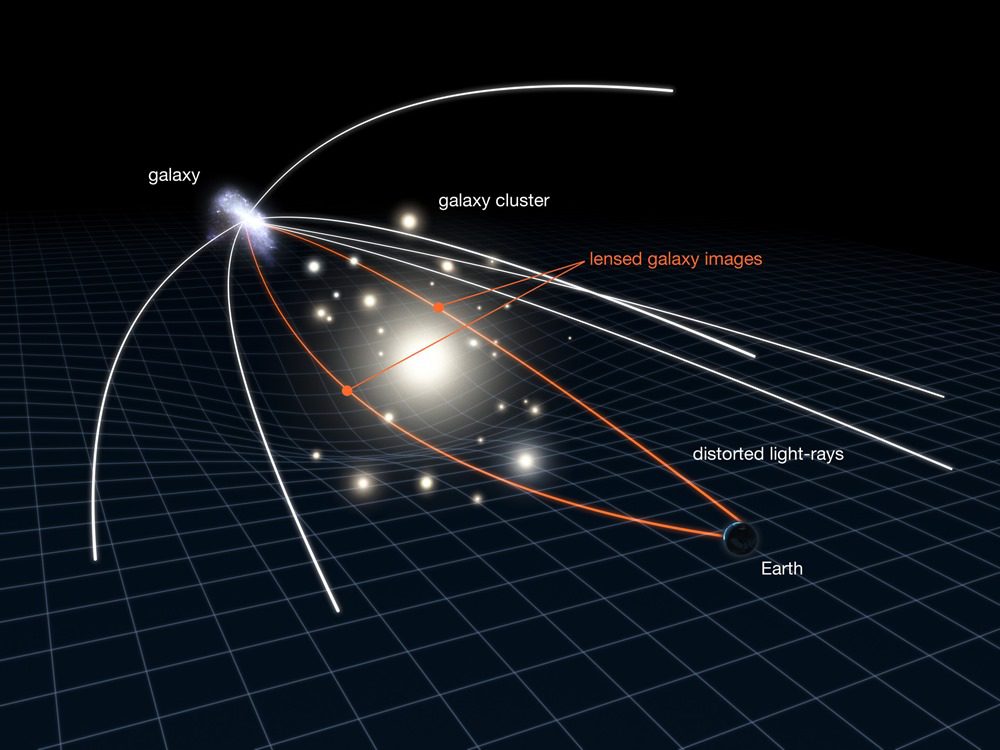
Incredible accuracy and Webb sensitivity (plus happy natural zoom due to the effect gravity lens a galaxy in the foreground) made it possible to observe these “sparks” for the first time, which were instruments Hubble (Ancestor Webb) It wouldn’t have happened. Thanks to multi-wavelength observations of the clusters, scientists can better model and understand their physical properties, such as their age and the number of stars they contain.
This illustration shows a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, which astronomers use to study very distant and very faint galaxies. (NASA/ESA/El Calcada)
For very distant and very ancient globular clusters, this presents an opportunity to peek at the “monsters” of the very ancient universe.
According to Mola:
These newly identified clusters formed near the time when stars could first be formed. Since the Sparkler Galaxy is so far away from our Milky Way, it is easy to determine the age of its globular clusters. We observe Sparkler as it was 9 billion years ago, when the universe was only 4.5 billion years old.
As Webb stares into space, we can expect to learn more about the origins of our universe, and ultimately about ourselves.
The study, published in Astrophysical Journal Letters: Sparkler: advanced red high-displacement globular cluster filters captured by JWST Presented on the University of Toronto website: Dunlap researchers help reveal a galaxy sparkling with the oldest star clusters in the universe.

“Hardcore beer fanatic. Falls down a lot. Professional coffee fan. Music ninja.”







More Stories
A documentary film denouncing the destruction of the planet
Robert Sovi Institute for Occupational Health and Safety Research
Starliner's first manned flight in May